1. Overview
- Tries are used to store dynamic set of strings, where retrieval and prefix matching are efficient
- A trie is made up of nodes, where each node represents a single character in a string
Advantages:
- Efficient Search: Ideal for searching words by prefix, taking
O(m)time, wheremis the length of the word - Memory Efficient for Common Prefixes: Saves memory by sharing prefixes among words
Applications:
- Autocomplete systems
- Spell checkers
- IP routing (Longest prefix matching)
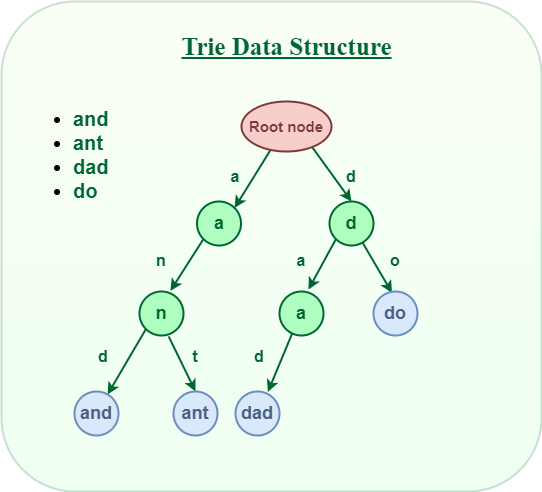
2. Structure
Each node in a Trie represents a single character and may have several children for each character that follows. The end of a word is typically marked with a boolean flag.
struct TrieNode {
TrieNode* children[26]; // Assuming only lowercase English letters (a-z)
bool isEndOfWord; // Marks the end of a word
TrieNode() {
isEndOfWord = false;
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
children[i] = nullptr;
}
}
};Example Trie
For words cat, car, and dog:
- Root node branches into
candd cbranches intoa, then intotandrdbranches intoo, then intog
(root)
/ \
c d
/ \ \
a o o
/ \ \ \
t r g g
(end)(end) (end)
3. Operations
| Operation | Description | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insert | Inserts a word into the trie | O(m) | O(m * n) |
| Search | Checks if a word exists in the trie | O(m) | O(1) |
| Starts With | Checks if a prefix exists in the trie | O(m) | O(1) |
Where m is the length of the word being inserted of searched, and n is the number of words in the Trie
4. Implementation
4.1 Insert
How It Works:
- Starts from the root, and for each character in the word:
- If the character node doesn’t exist, create it
- Move to the next character node
- Mark the end of the word
void insert(TrieNode* root, const string& word) {
TrieNode* node = root;
for(char ch : word) {
int index = ch - 'a';
if(!node->children[index]) {
node->children[index] = new TrieNode();
}
node = node->children[index];
}
node->isEndOfWord = true;
}4.2 Search
How It Works:
- Traverse the Trie based on each character of the word
- If a ndoe for any character is missing, the word isn’t in the Trie
- If all characters are found, check if the last node marks the end of a word
bool search(TrieNode* root, const string& word) {
TrieNode* node = root;
for(char ch : word) {
int index = ch - 'a';
if(!node->children[index]) {
return false;
}
node = node->children[index];
}
return node->isEndOfWord;
}4.3 Starts With (Prefix Search)
How It Works:
- Traverse the Trie based on each character of the prefix
- If a node for any character is missing, the prefix isn’t in the Trie
- If all character are found, the prefix exists
bool startsWith(Trie* root, const string& prefix) {
TrieNode* node = root;
for(char ch : word) {
int index = ch - 'a';
if(!node->children[index]) {
return false;
}
node = node->children[index];
}
return true;
}