Min Heap & Max Heap
1. Overview
-
Heap: a complete binary tree where each parent node follows a specific order property with its children
- commonly used to implement a Priority Queue as heaps provide efficient access to the highest (or lowest) priority element
-
Types:
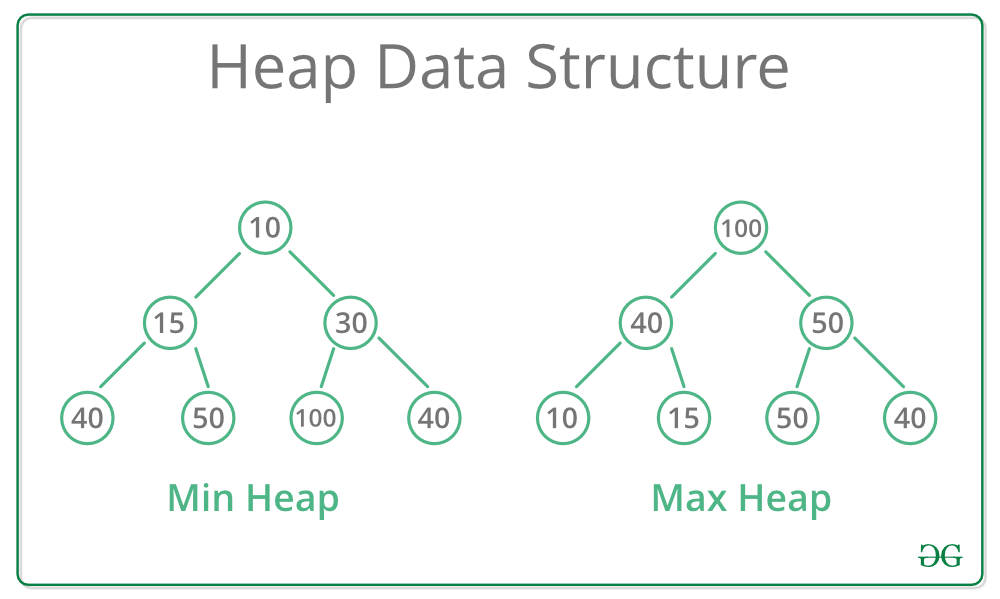
- Min Heap: Parent nodes are less than or equal to their children
- Max Heap: Parent nodes are greater than or equal to their children
-
Properties:
- Complete Tree: All levels are fully filled except possibly the last level, which is filled from left to right
- Heap Property: Ensures that the smallest or largest element is always the root
-
Common Applications ⇒ provides efficient access to the highest (or lowest) priority element
- Priority Queues
- Graph Algorithms: Dijkstra’s Shortest Path Algorithm, Prim’s Minimum Spanning Tree
- Heap Sort
2. Structure
- Typically represented using an array for space efficiency:
- Left child of node at index
iis at2 * i + 1 - Right child of node at index
iis at2 * i + 2 - Parent of node at index
iis at(i - 1) / 2
- Left child of node at index
Example Array Representation
For a Min Heap with elements [1, 3, 6, 5, 9, 8]:
1
/ \
3 6
/ \ /
5 9 8
3. Operations
| Operation | Description | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | Adds a new element while maintaining heap order | O(log n) |
| Extract | Removes the root element (min in Min Heap, max in Max Heap) and reorders the heap | O(log n) |
| Peek | Returns the root element without removing it | O(1) |
| Heapify | Covnerts an arbitrary array into a valid heap | O(n) |
4. Implementation
4.1 Insert
How It Works:
- insert the new element at the end of the heap (maintains the complete tree property)
- bubble up: compare the inserted element with its parent
- if it violates the heap property, swap it with the parent and repeat until the heap property is restored
void insert(vector<int>& heap, int value) {
heap.push_back(value);
int i = heap.size() - 1;
while (i != 0 && heap[(i - 1) / 2] > heap[i]) { // Min Heap
swap(heap[i], heap[(i - 1) / 2]);
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
}4.2 Extract Min / Max
How It Works:
- removes the root element (min or max)
- move the last element to the root position
- bubble down (heapify): compare the new root with its children, swap with the smaller (Min Heap) or larger (Max Heap) child if it violates the heap property, and repeat until the heap is valid
int extractMin(vector<int>& heap) {
if (heap.size() == 0) return -1;
if (heap.size() == 1) {
int root = heap[0];
heap.pop_back();
return root;
}
int root = heap[0];
heap[0] = heap.back();
heap.pop_back();
int i = 0;
int n = heap.size();
while (true) {
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
int smallest = i;
if (left < n && heap[left] < heap[smallest]) smallest = left;
if (right < n && heap[right] < heap[smallest]) smallest = right;
if (smallest != i) {
swap(heap[i], heap[smallest]);
i = smallest;
} else break;
}
return root;
}int extractMax(vector<int>& heap) {
//implement here
}4.3 Peek (Get Min / Max)
- Returns the root of the heap, which is the minimum element in a Min Heap or the maximum in a Max Heap
- Time Complexity:
O(1)
4.4 Heapify
- Converts an arbitrary array into a valid heap by starting from the last non-leaf node and applying the bubble-down operation
void heapify(vector<int>& heap, int n, int i) {
int smallest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
if (left < n && heap[left] < heap[smallest]) smallest = left;
if (right < n && heap[right] < heap[smallest]) smallest = right;
if (smallest != i) {
swap(heap[i], heap[smallest]);
heapify(heap, n, smallest);
}
}
void buildHeap(vector<int>& heap) {
int n = heap.size();
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(heap, n, i);
}
}5. Heap Data Structure in C++ STL
- using
std::priority_queue - header
<queue> - container type: by default,
std::priority_queueuses a max-heap - a custom comparator can be used to convert it to a min-heap
Default Implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
int main() {
// Max Heap by default
std::priority_queue<int> maxHeap;
maxHeap.push(10);
maxHeap.push(20);
maxHeap.push(5);
std::cout << "Max element: " << maxHeap.top() << std::endl; // Outputs 20
maxHeap.pop(); // Removes 20
std::cout << "Next max element: " << maxHeap.top() << std::endl; // Outputs 10
return 0;
}Min Heap Implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
int main() {
// Min Heap using greater<int> comparator
std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int>> minHeap;
minHeap.push(10);
minHeap.push(20);
minHeap.push(5);
std::cout << "Min element: " << minHeap.top() << std::endl; // Outputs 5
minHeap.pop(); // Removes 5
std::cout << "Next min element: " << minHeap.top() << std::endl; // Outputs 10
return 0;
}Building a Heap From Existing List
- if you have an existing list (
std::vector) and want to convert it into a heap, you can use heap algorithms from the<algorithm>library:
- Make a Heap: Converts a list into a heap
- Push to Heap: adds a new element to a heap
- Pop from Heap: Removes the root element
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main() {
std::vector<int> nums = {10, 20, 5, 30};
// Make a Max Heap
std::make_heap(nums.begin(), nums.end());
std::cout << "Max element: " << nums.front() << std::endl; // Outputs 30
// Add a new element and re-heapify
nums.push_back(25);
std::push_heap(nums.begin(), nums.end());
std::cout << "New max element: " << nums.front() << std::endl; // Outputs 30
// Remove the max element and re-heapify
std::pop_heap(nums.begin(), nums.end());
nums.pop_back();
std::cout << "Max element after pop: " << nums.front() << std::endl; // Outputs 25
return 0;
}STL Operations
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
std::priority_queue | Implements a heap-based priority queue (Max Heap by default) |
std::make_heap | Converts a list into a heap |
std::push_heap | Adds a new element and maintains heap structure |
std::pop_heap | Removes the root element and maintains heap structure |
std::sort_heap | Sorts the elements in the heap in ascending order |