Traversal Trees DFS BFS
1. Overview
- Tree traversal is the process of visiting each node in a binary tree exactly once.
- There are two main categories:
- Depth-First-Search (DFS): Explores as deep as possible along each branch before Backtracking .
- Breadth-First-Search (BFS): Visits nodes level-by-level from top to bottom.
2. Traversal Types and Use Cases
| Traversal Type | Order | Use Case |
|---|
| In-order | Left → Root → Right | Retrieve elements insorted order (BST). |
| Pre-order | Root → Left → Right | Copy or serialize a tree. |
| Post-order | Left → Right → Root | Delete a tree or evaluate postfix expressions. |
| Level-order | Top to Bottom (Level-wise) | Explore hierarchical structures or find shortest paths. |
3. Depth-First Search
3.1 In-order Traversal
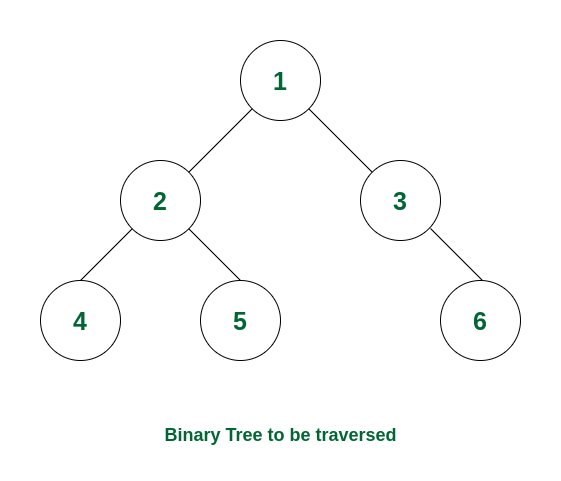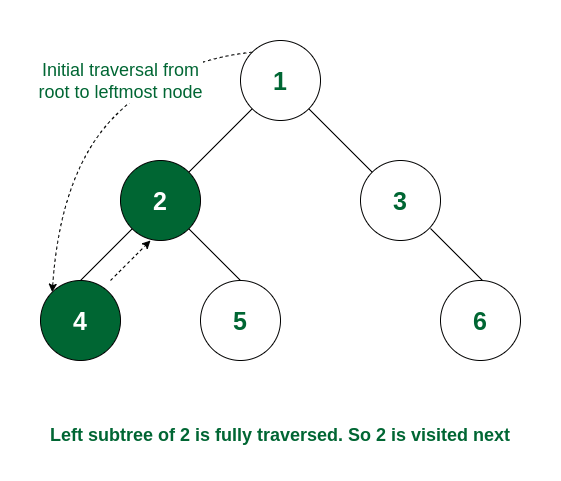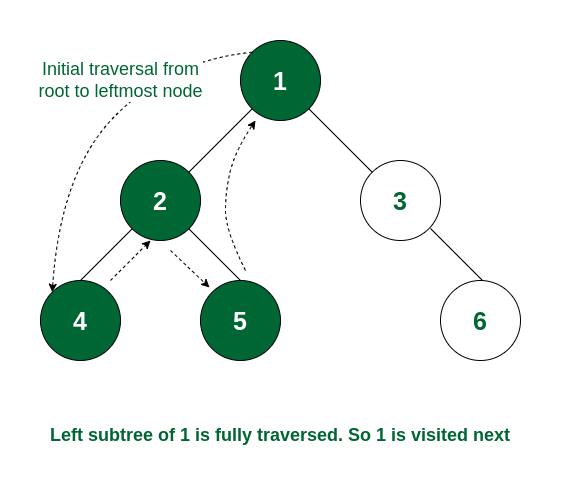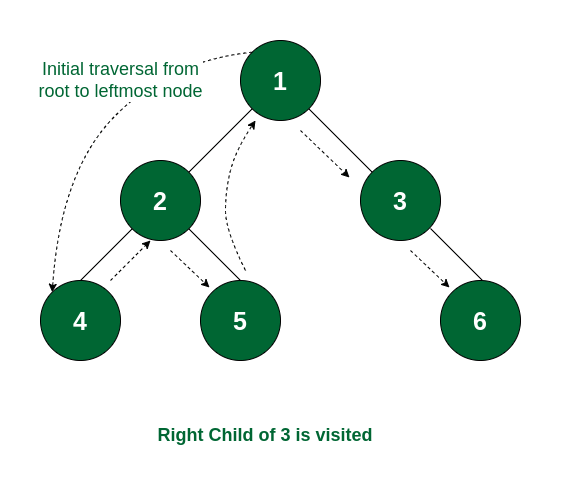
How it Works:
- Start with the root node
- Recursively visit the left subtree until reaching the leftmost node
- Print the node once the left child has been processed
- Move to the right subtree and repeat
Implementation
void inorder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return;
inorder(root->left);
std::cout << root->data << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
3.2 Pre-order Traversal
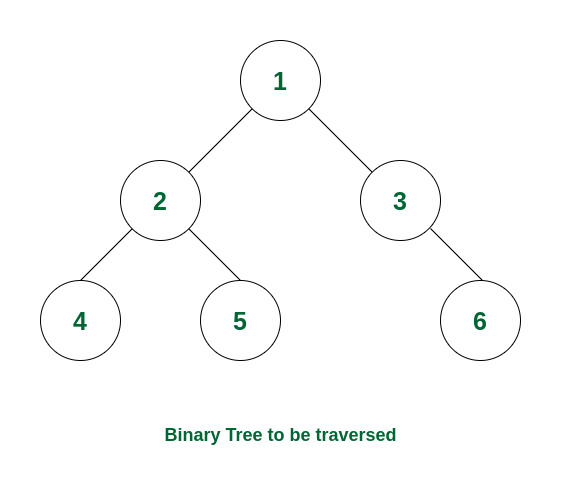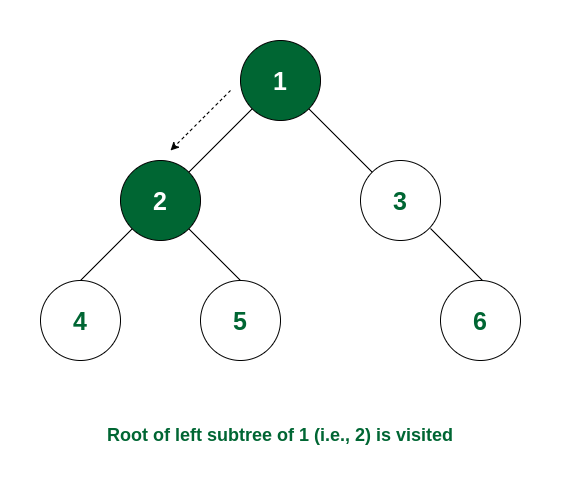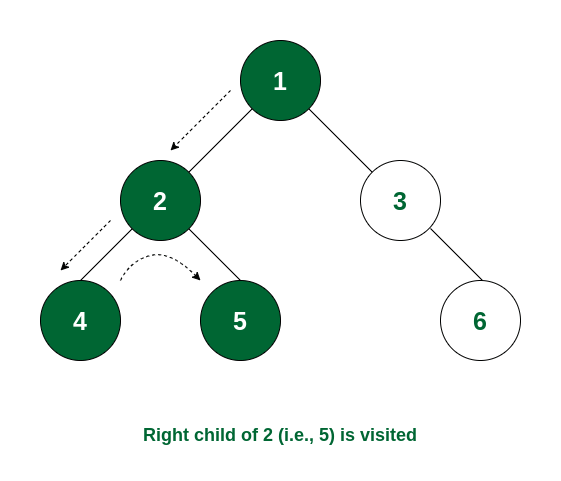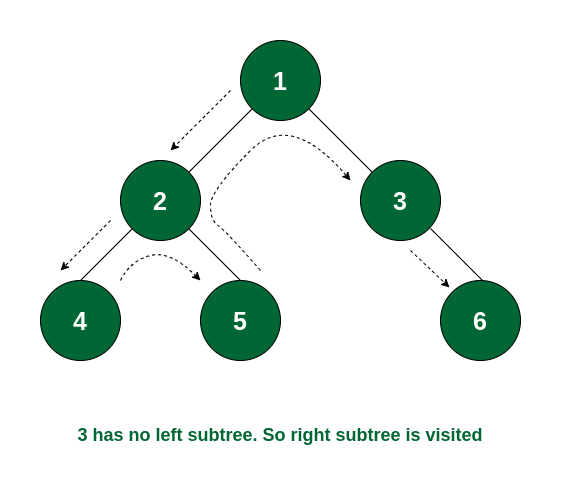
How it Works:
- Start at the root node and print it
- Move to the left subtree and recursively traverse it
- Once the left subtree is done, move to the right subtree
Implementation
void preorder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return;
std::cout << root->data << " ";
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);
}
3.3 Post-order Traversal
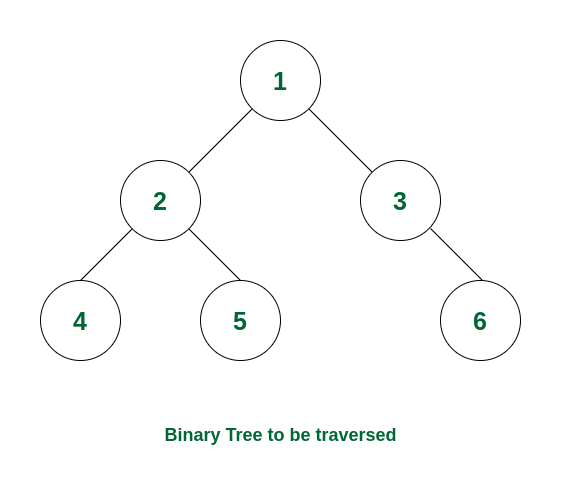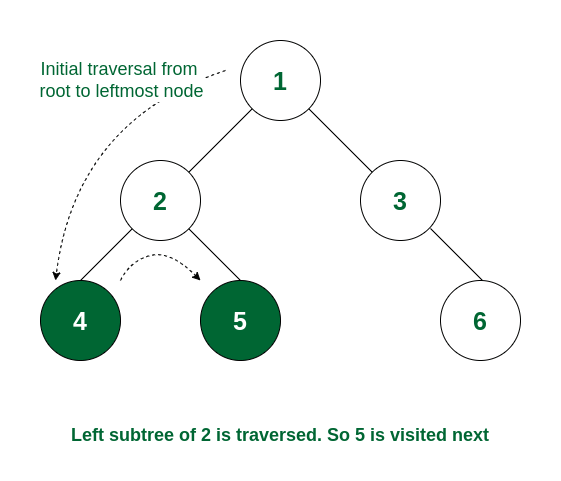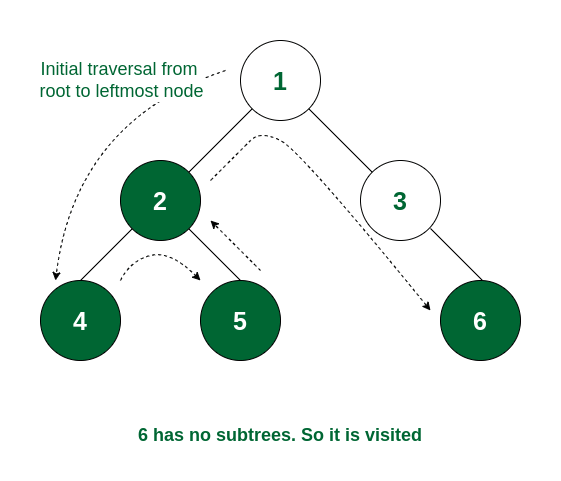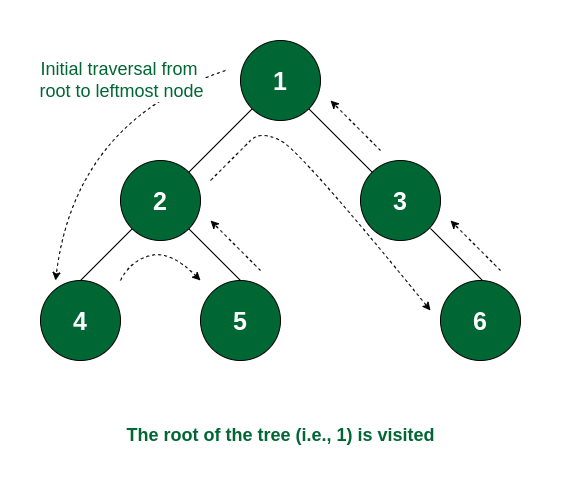
How it Works:
- Recursively visit the left subtree
- Once done, visit the right subtree
- After both subtrees are processed, print the current node
- this traversal is useful when nodes must be processed after their children (e.g., deletion)
Implementation
void postorder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return;
postorder(root->left);
postorder(root->right);
std::cout << root->data << " ";
}
4. Breadth-First Search
4.1 Level-order Traversal
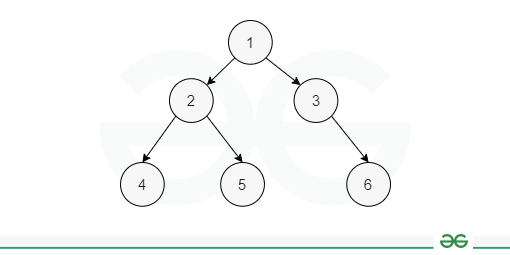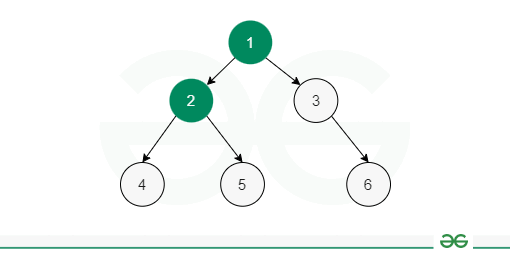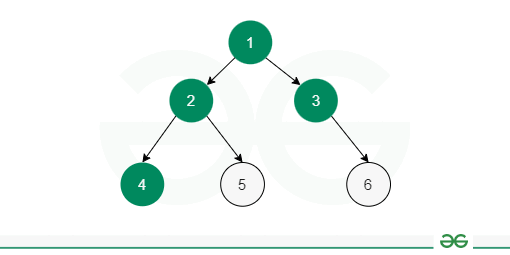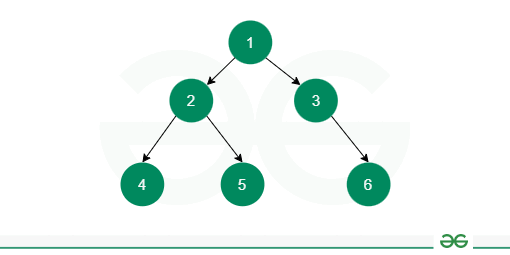
How it Works:
- Use a queue to keep track of nodes at each level
- Start with the root node in the queue
- Process the front node from the queue and print it
- Enqueue the left and right children of the current node (if they exist)
- Repeat until the queue is empty
Implementation
void levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return;
std::queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* current = q.front();
q.pop();
std::cout << root->data << " ";
if(current->left != nullptr) q.push(current->left);
if(current->right != nullptr) q.push(current->right);
}
}



