Path-Finding Shortest-Path Weighted-Graphs Graphs
1. Overview
- Finds the shortest path from a source node to all other nodes in a graph with non-negative weights
- Graph Type: Weighted, directed or undirected graph with non-negative weights
- Data Structure: Uses a Priority Queue (min-heap) to store nodes based on their current shortest distance from the source
- Approach: Greedy algorithm that explores the shortest paths first
- Time Complexity: O((V + E) log V)
- since the extraction of the minimum element from the heap is of O(log V)
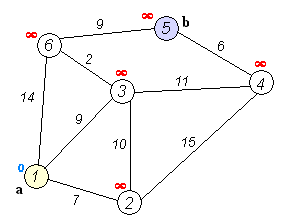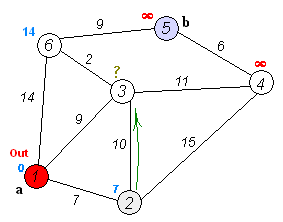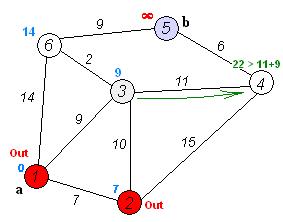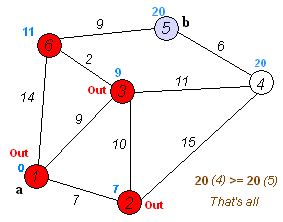
2. Algorithm Steps
- Initialize:
- Set the distance to the source node as 0 and all other nodes as
infinity - Use a priority queue (min-heap) to keep track of nodes with the minimum distance
- Process the Current Node:
- Extract the node with the smallest distance from the priority queue
- For each of its adjacent nodes
- Calculate the distance from the source node to this adjacent node
- If this calculated distance is smaller than the known distance, update the distance and add the node to the priority queue
- Repeat until the priority queue is empty
- Output the shortest distance from the source node to each other node
3. Implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <utility>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
vector<int> dijkstra(int V, vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> &adj, int src) {
vector<int> dist(V, numeric_limits<int>::max()); // Initialize distances as infinite
dist[src] = 0;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> pq;
pq.push({0, src}); // {distance, vertex}
while (!pq.empty()) {
int u = pq.top().second;
int uDist = pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
if (uDist > dist[u]) continue; // Skip if distance is outdated
for (auto &neighbor : adj[u]) {
int v = neighbor.first;
int weight = neighbor.second;
if (dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pq.push({dist[v], v});
}
}
}
return dist;
}